-
1. Which types of fracture would be suspicious for a non-accidental injury in a child?
Show Answer
Correct answer:
- Fractures in pre-mobile children (under 18 months)
- Humeral/femoral fractures in an under 3-year-old
See Chapter 40.
-
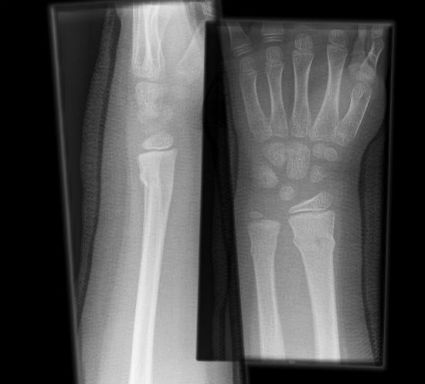
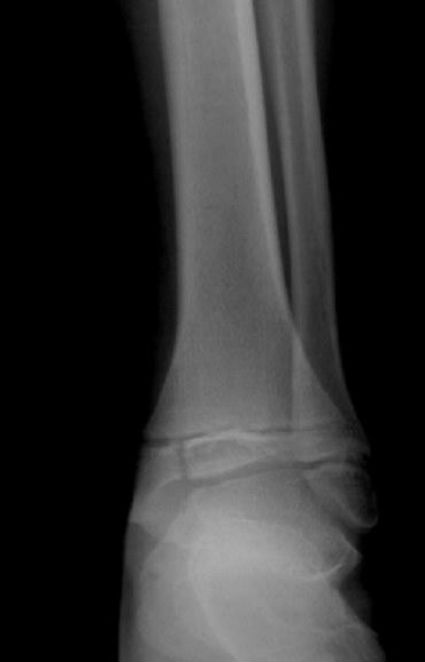
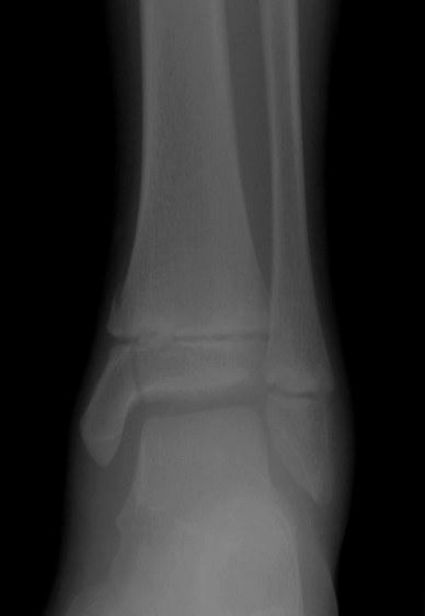
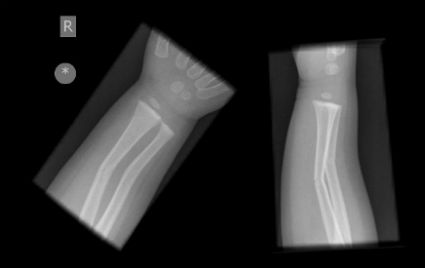
2. Match the fracture type to the X-ray.
(a) Greenstick
(b) Salter Harris III
(c) Buckle
(d) Salter Harris IV
Show Answer
Show/Hide Scan of X-ray 1
Show/Hide Scan of X-ray 2
Show/Hide Scan of X-ray 3
Show/Hide Scan of X-ray 4
Correct answer:
X-ray 1: Buckle fracture distal radius and ulna.
X-ray 2: Salter Harris III.
X-ray 3: Salter Harris IV.
X-ray 4: Greenstick fractures.
See Chapter 40.
-
3. At which ages are the following causes of a limp most common?
(a) Transient synovitis.
(b) Slipped upper femoral epiphysis.
(c) Perthes' disease.
(d) Toddler's fracture.
Show Answer
Correct answer:
(a) Transient synovitis.
3–10 years
(b) Slipped upper femoral epiphysis.
>10 years
(c) Perthes' disease.
4–8 years
(d) Toddler's fracture.
1–3 years
See Chapter 41.
-
4. On examination of a febrile child, what features would warrant immediate referral/treatment?
Show Answer
Correct answer:
- Pallor, mottling, ashen, cyanosis
- No response to social cues
- Weak, high-pitched or continuous cry
- Lethargy or difficult to rouse
- Grunting, tachypnoea >60 or increased work of breathing
- Non-blanching rash
See Chapter 42.
-
5. A 2-year-old boy presents after ingesting a button battery 1 h earlier. How would you manage this child?
Show Answer
Correct answer:
(a) Arrange X-ray of chest (and abdomen if not visible on chest X-ray)
(b) If in oesophagus, refer for removal
If below diaphragm, eat and drink and re-X-ray in 12 h
(c) If fragmented or not moved, refer for removal
If moved position along bowel, discharge with advice to return if symptomatic
See Chapter 43.
-
6. List the common childhood exanthems.
Show Answer
Correct answer:
- Measles
- Rubella
- Varicella (chickenpox)
- Fifth disease
- Roseola
See Chapter 44.
-
7. Name the rash described by each of the following characteristics.
(a) Crops of lesions at varying stages, including crusted scabs, vesicles and papules.
(b) Red cheeks and a red, lacy rash in the upper arms and legs.
(c) Umbilicated pearly or skin-coloured papules.
(d) Non-blanching, rapidly developing rash in an unwell, feverish child.
Show Answer
Correct answer:
(a) Crops of lesions at varying stages, including crusted scabs, vesicles and papules.
Varicella
(b) Red cheeks and a red, lacy rash in the upper arms and legs.
Erythema infectiosum/slapped cheek
(c) Umbilicated pearly or skin-coloured papules.
Molluscum contagiosum
(d) Non-blanching, rapidly developing rash in an unwell, feverish child.
Meningocococcal septicaemia
See Chapter 44.