Haematology
at a Glance
Fourth EditionAtul B. Mehta and A. Victor Hoffbrand
Case Studies
Case 15: A 2-year-old child with failure to thrive
A 2-year-old girl, born of Greek parents, is referred for investigation. Her parents are concerned that she is generally unwell. She is small for her age, is tired, sleeps excessively, and her GP is concerned that she is not meeting her developmental milestones.
On examination she is noted to have a prominent forehead, a widened nose and is pale. The spleen is palpable.
Investigations show:
Hb 45 g/L
MCV 62 fl
WBC 23 × 109/L
Platelets 456× 109/L.
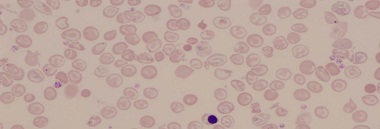
Blood film – as illustrated.
-
(a) What does the blood film show?
-
(b) What is the likely diagnosis?
-
(c) How is the diagnosis confirmed?
-
(d) What complications can occur?
-
(e) What is the treatment?