- Home
- Cases
- Revision notes
- Further online reading
- Figures
- Your feedback
- Become a reviewer
- 'at a Glance' series
- More student books
- Student Apps
- Join an e-mail list

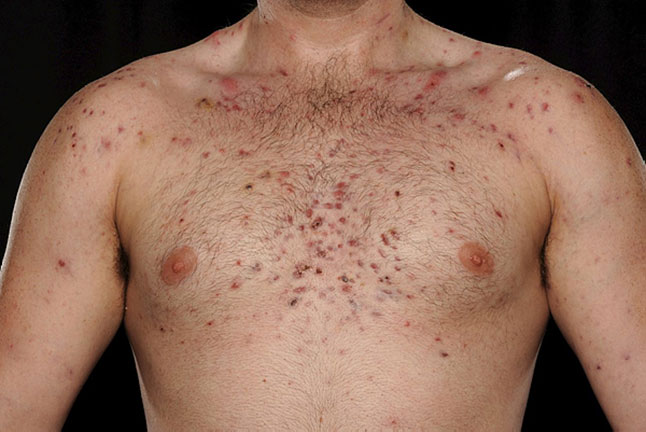
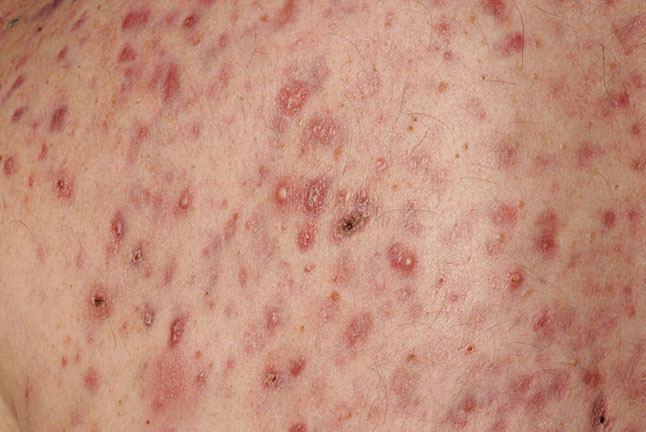
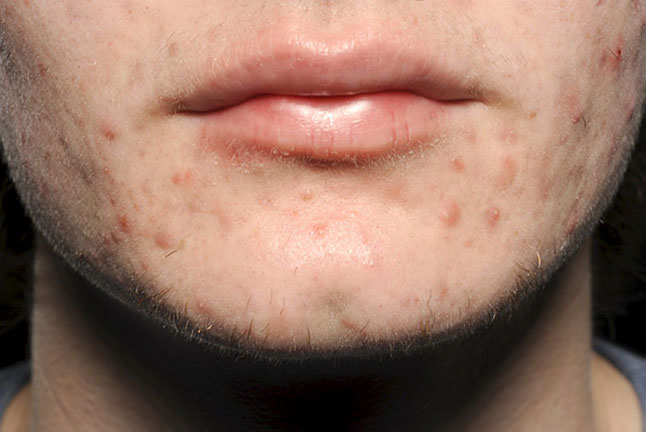
This 22-year-old man presented with worsening spots with scarring on his face, chest and back since his mid teens. He did not feel the creams and antibiotic tablets his GP prescribed 6 months ago had improved his rash. He was a sports enthusiast and was otherwise well.
(a) What is the most likely diagnosis?
(b) What are the hallmark clinical features of this condition?
(c) What are the potential complications of this skin disease being left untreated?
(d) What is the aetiology of this skin condition?
(e) What possible underlying causes should be considered as a cause of this rash in individuals with severe and/or treatment-resistant disease?
(f) How would you manage this patient?
(g) What other treatment option is available for a female patient with this disease?
(h) What special precautions should be taken in females with this disease being considered for systemic therapy?
See Chapter: 14.