-
Step 1: define the treatment goal
Show Answer
Model answer: Reduce gastric pH and promote ulcer healing
-
Step 2: compare drug classes for ideal treatment
Show Answer
Model answer: Available classes are: antacids, H2-antagonists, proton pump inhibitors.
They can be compared as follows:
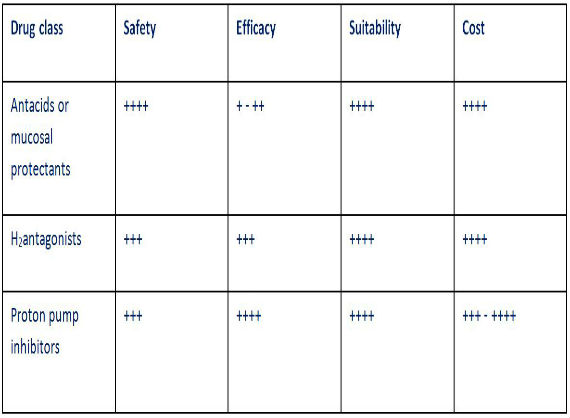
Case Study Figure 12
From this analysis, a proton pump inhibitor would be the best choice
-
Step 3: compare individual drugs in chosen class
Show Answer
Model answer: A number of proton pump inhibitors are available:
Omeprazole, lansoprazole, pantoprazole, rabeprazole, esomeprazole.
In real life practice there is probably little difference between the PPIs except cost. There are some data to suggest rabeprazole and esomeprazole may be more effective. Additionally, omeprazole has more drug-drug interactions.
Choice should normally be made by consulting the local formulary.
-
Step 4: suitability of chosen drug for patient
Show Answer
Model answer: As this patient is not noted to be on any other medicines, drug‒drug interactions are not a concern.
Lower doses are not necessary for elderly patients.
Intravenous therapy may be desirable initially - omeprazole, esomeprazole and pantoprazole are available as i.v. preparations.
-
Step 5: choose dose, frequency, route
Show Answer
Model answer: Oral therapy may be less effective in major bleeding (although this patient has 'minor' bleeding), and the oral route may not be suitable if the patient is not to have oral intake. Intravenous therapy may be preferable.
Higher doses are initially used and reduced after time to a maintenance dose if needed.
Omeprazole 40 mg once a day intravenously would be one suitable regime.
-
Step 6: monitor effects
Show Answer
Model answer: Duration of therapy should be the shortest possible with the lowest possible dose - longer term issues of hypomagnesaemia, tendency to Costridium difficile infection and fractures in the elderly are seen. These should be looked for, particularly if treatment is for more than one year. Beneficial effects can be monitored by asking about symptoms.

